 文章正文
文章正文
# Keywords - English Writing on Key Terms in
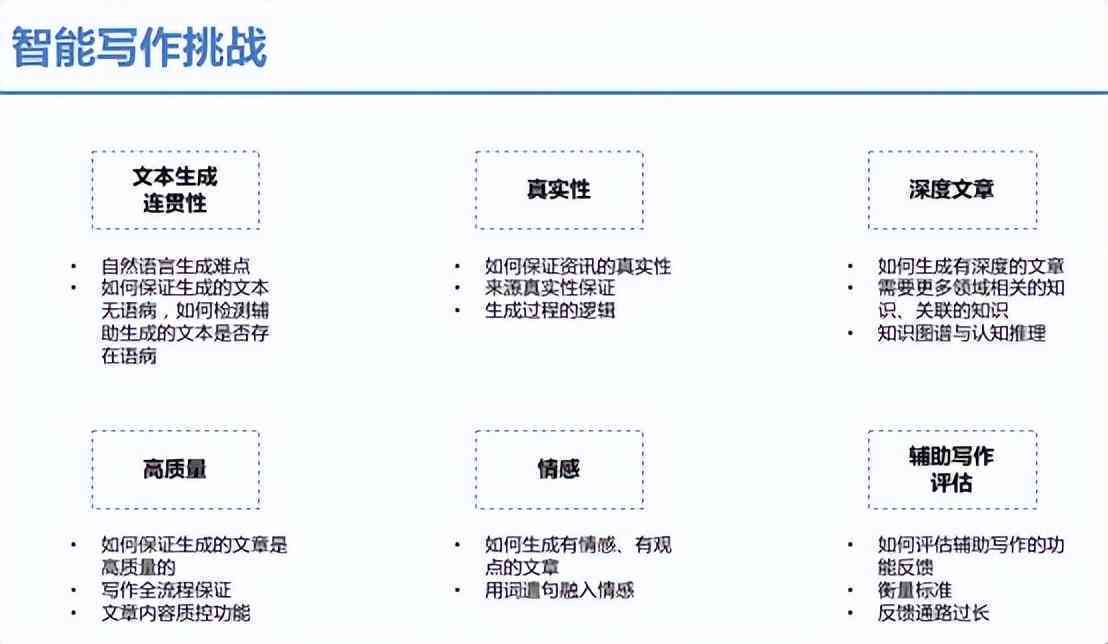
## Introduction
The rapid advancement of technology has brought about significant changes in our dly lives. Artificial Intelligence () is one of the most transformative technologies, impacting various sectors such as healthcare, transportation, and entertnment. As continues to evolve, it brings with it a plethora of terms and concepts that can be overwhelming for beginners. This article ms to demystify some of the key terms in the field of , providing a comprehensive guide to help you navigate through the complex world of .
## On-Device
One of the emerging trends in is On-Device , also known as Edge . This roach involves deploying models directly on mobile devices or IoT (Internet of Things) devices, rather than relying solely on cloud-based processing. By doing so, On-Device offers several advantages:
1. Reduced Latency: Since computations are performed locally, there is no need for data to travel to the cloud, resulting in faster response times.
2. Privacy Protection: Processing data on-device ensures that sensitive information remns within the device, enhancing privacy.
3. Cost Efficiency: Reducing reliance on cloud services can lead to lower operational costs, especially for businesses with large user bases.
4. Bandwidth Conservation: By minimizing data transfer between devices and the cloud, On-Device helps conserve bandwidth, which is particularly beneficial in areas with limited connectivity.
Example Scenario
Imagine you are using a smartphone that uses to recognize objects in real-time. With On-Device , the can perform this task without sending your photos to the cloud, thereby ensuring faster and more secure processing.
## Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) is at the core of , enabling machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time. It involves algorithms that can analyze and interpret data, make predictions, and take actions based on patterns and insights derived from the data.
Types of Machine Learning
1. Supervised Learning: In supervised learning, the algorithm is trned on labeled data, meaning each trning example is pred with an output label. The goal is to learn a ming from inputs to outputs so that the model can predict outputs for new, unseen data.
*Example*: Classifying emls as spam or not spam based on labeled examples.
2. Unsupervised Learning: Unlike supervised learning, unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled data. The algorithm tries to find hidden patterns or intrinsic structures in the input data.
*Example*: Clustering customers into different groups based on purchasing behavior.
3. Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning involves an agent interacting with an environment to learn the best actions to take in order to maximize a reward.
*Example*: Trning a robot to navigate a maze by rewarding it for reaching the end.
Atmosphere: The Power of Algorithms
Imagine a world where algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data in seconds, uncovering patterns that humans might miss. This atmosphere of efficiency and insight is what machine learning brings to the table.
## Deep Learning


Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers (deep neural networks) to learn and extract features from complex data. These networks can automatically discover intricate patterns and representations in data, making them highly effective for tasks like image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing.
Atmosphere: The Complexity of Neural Networks
In a world where neural networks can process millions of parameters, the complexity is staggering. The atmosphere here is one of awe and wonder at the capabilities of these advanced models.
Example Scenario
Consider a self-driving car that uses deep learning to recognize traffic signs and pedestrians. The car's onboard system processes video feeds in real-time, identifying crucial elements to ensure safe navigation.
## Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of that focuses on the interaction between computers and human languages. NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, making it possible for chatbots, virtual assistants, and translation tools to operate seamlessly.
Subfields of NLP
1. Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing text to determine the emotional tone behind words, often used in social media monitoring and customer feedback analysis.
*Example*: A company using sentiment analysis to gauge public opinion about its products.
2. Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifying and categorizing key information in text, such as names, organizations, and locations.
*Example*: Extracting important detls from news articles for summarization.
3. Machine Translation: Converting text from one language to another, facilitating global communication.
*Example*: Google Translate translating a document from English to Spanish.
Atmosphere: The Complexity of Language

In a world where languages are diverse and nuanced, NLP algorithms must navigate a complex landscape of grammar, syntax, and cultural context. The atmosphere here is one of challenge and triumph, as these models strive to bridge the gap between human and machine understanding.
## Computer Vision
Computer Vision is a field of that focuses on enabling computers to interpret and understand visual information from the world. It involves tasks like image recognition, object detection, and scene reconstruction, with lications ranging from medical imaging to autonomous driving.

Subfields of Computer Vision
1. Image Classification: Categorizing images into predefined classes, such as identifying whether an image contns a cat or a dog.
*Example*: An that can identify different types of flowers from photos taken by users.
2. Object Detection: Locating and identifying multiple objects within an image, providing bounding boxes around each detected object.
*Example*: A security camera system that detects intruders in a restricted area.
3. Semantic Segmentation: Dividing an image into meaningful segments, assigning labels to each pixel.
*Example*: Medical imaging software that identifies different tissues in an MRI scan.
Atmosphere: The Visual World

In a world where every moment is captured in pixels, computer vision algorithms must parse and interpret this visual data to make sense of the world. The atmosphere here is one of discovery and innovation, as these models bring clarity to the visual chaos around us.
## Robotics
Robotics combines with mechanical engineering to create intelligent machines capable of performing complex tasks. Robots can be programmed to interact with their environment, manipulate objects, and even learn from experience, making them valuable in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and space exploration.
lications of Robotics

1. Industrial Automation: Using robots for repetitive tasks in factories, improving efficiency and reducing human labor.
*Example*: A robotic arm assembling parts on a production line.
2. Medical Assistance: Employing robots in surgeries and patient care, offering precision and consistency.
*Example*: A surgical robot performing minimally invasive procedures.

3. Space Exploration: Sending robots to explore distant planets and moons, collecting data and samples.
*Example*: NASA’s Mars rovers conducting scientific research on the Martian surface.
Atmosphere: The Precision of Machines
In a world where precision is paramount, robotics brings the power of automation and intelligence to physical tasks. The atmosphere here is one of precision and control, as robots execute tasks with accuracy and reliability.
## Conclusion
As we delve deeper into the realm of , it becomes increasingly important to understand the key terms and concepts that define this rapidly evolving field. From On-Device to Robotics, each term represents a piece of the puzzle that makes up the broader picture of artificial intelligence. By familiarizing ourselves with these concepts, we can better reciate the transformative impact is having on our world and prepare for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
---
This article provides a foundational understanding of keywords, helping readers navigate the complex and fascinating world of artificial intelligence. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply someone curious about the future of technology, this guide will serve as a valuable resource in your journey to comprehend and engage with .